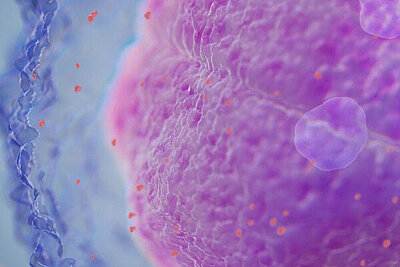
A patient case of an early response of the innate immune system to an active infection by intracellularly located bacteria is described. Additional information from inflammation parameters such as activated neutrophils and reactive lymphocytes support an early diagnosis so that targeted treatment can be started, changed or modified faster.
File type:
pdf
File size:
360 KB
Release:
05-03-24